City Co-Rescue
Post-earthquake information collection & release system
Overview
1. Current Rescue Method Study
Feature
· Investigators from governmental functional departments
Advantages
· Accurate information · With clear Goals · Professional evaluation
Disadvantages
· Intricate procedure · Low efficiency (Too many intermediaries)
Feature
· A direct way for victims to ask for help from the government
Advantages
· Communicate directly · Detailed Demands
Disadvantages
· Limited receiver · Phonetic description only
Feature
· Main communication window for the public after the earthquake
Advantages
· Extended coverage · Up to date · Large quantities of information
Disadvantages
· Key information easily overlooked · Imprecise information create panic
2. Challenge and Solution
Rescuers and decision makers have difficulties accessing on-site information.
Communication between various government departments is intricate.
Lacking of direct communication between the public and the government leads to information lag.
The Internet is the most widely and comprehensive way after earthquake. At the same time, the lack of information processing lead to low rescue efficiency. Hence, in the following research, we would further investigate the post-disaster information classification, information communication and information transmission based on the Internet.
Initial Research
Questionaire results
200 questionaires were distributed. 100 for the public and 100 for the government. 188 valid questionaires were received. 96 from government staff and 92 from urban residents.
Questions: What information is considered as the most important after an earthquake?
public:
government:
Question: What App is used to get information after an earthquake?
public:
government:
Question to Goverment:
What information do you need in your post-earthquake rescue efforts?
Question to public:
What kind of post-earthquake information are you willing to provide?
This result determines the initial layout of UI layers, from the most needed information to secondary information. According to the result, we choose Baidu Map App as our platform, which has a wide popularity, high usage rate and location system.
Define the Demand
This classification helps us determine the functions we should provide and their priorities. The public client mainly includes calling for rescue, reporting and navigating to nearby rescue spot, shelter, etc. The government client includes checking on-site data, working collaboratively and releasing information.
User Service Mapping
Reference:
Ozdamar L, Ekinci E, Kucukyazici B. Emergency logistics planning in nature desaster [J]. Annals of Operation Research, 2014, 129(4): 217-245.
Jae Y. Stochasitc scheduling problems for minimizing tardy jobs with application to emergency vehicle dispatching on unreliable road networks [D]. New York: L University of NewYork, 2003.
Carmen G.Rawls, Mark A, Turnquist. Pre-positioning of emergency supplies for disaster response [J]. Transportation Research Part B, 2010, 44(4): 521-534.
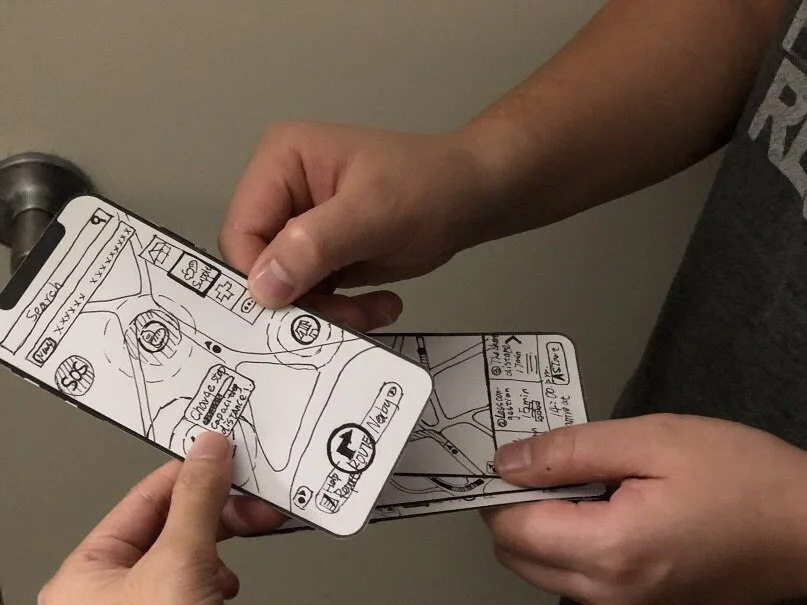
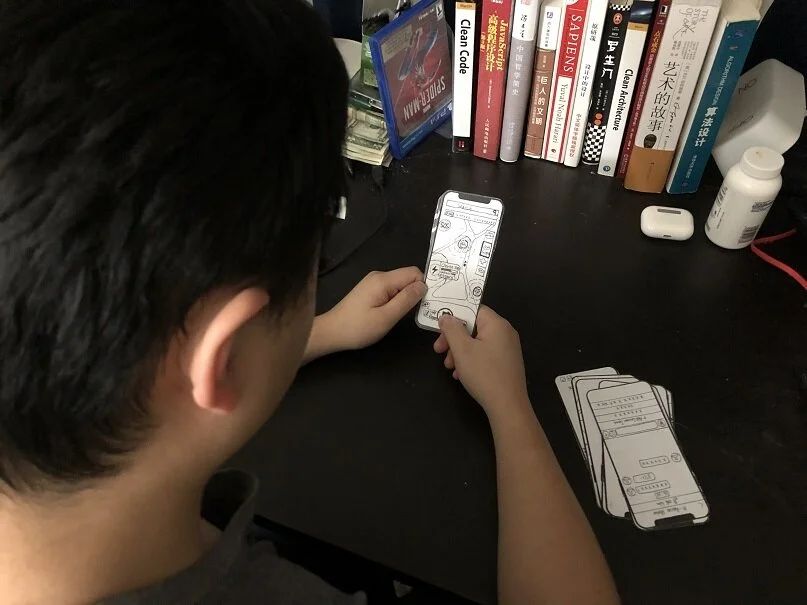
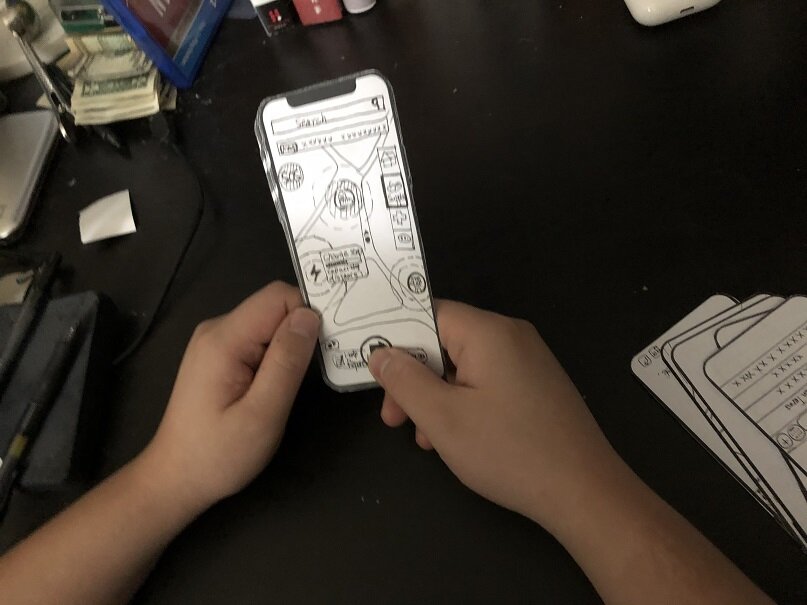
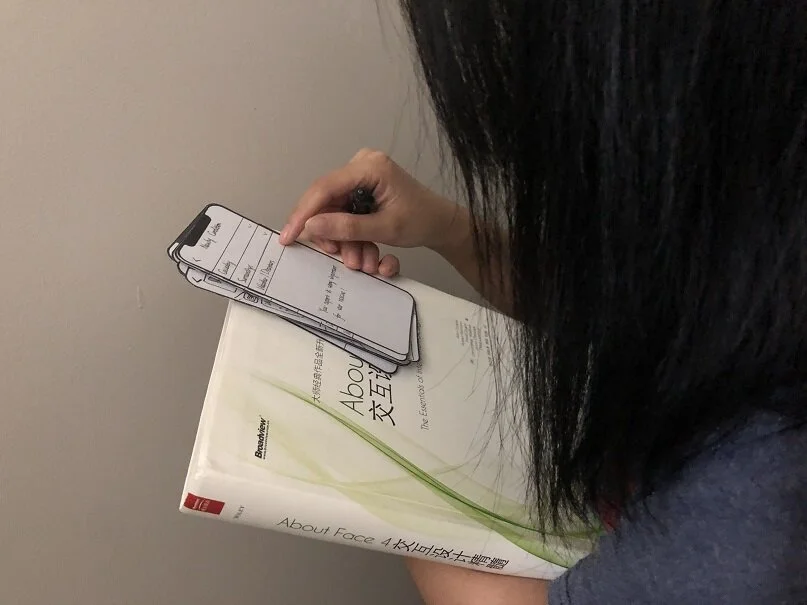
Story Board
Paper prototype & Usability testing
Testing insight 1:
The main functional area is not obvious enough to attract attention. Too many functions on the same page leads to confusion.
Testing insight 2:
The information provided by SOS function is insufficient. In the next stage, the communication function with rescuers would be added. And we would increase the weight of publishing official information.
Testing insight 3:
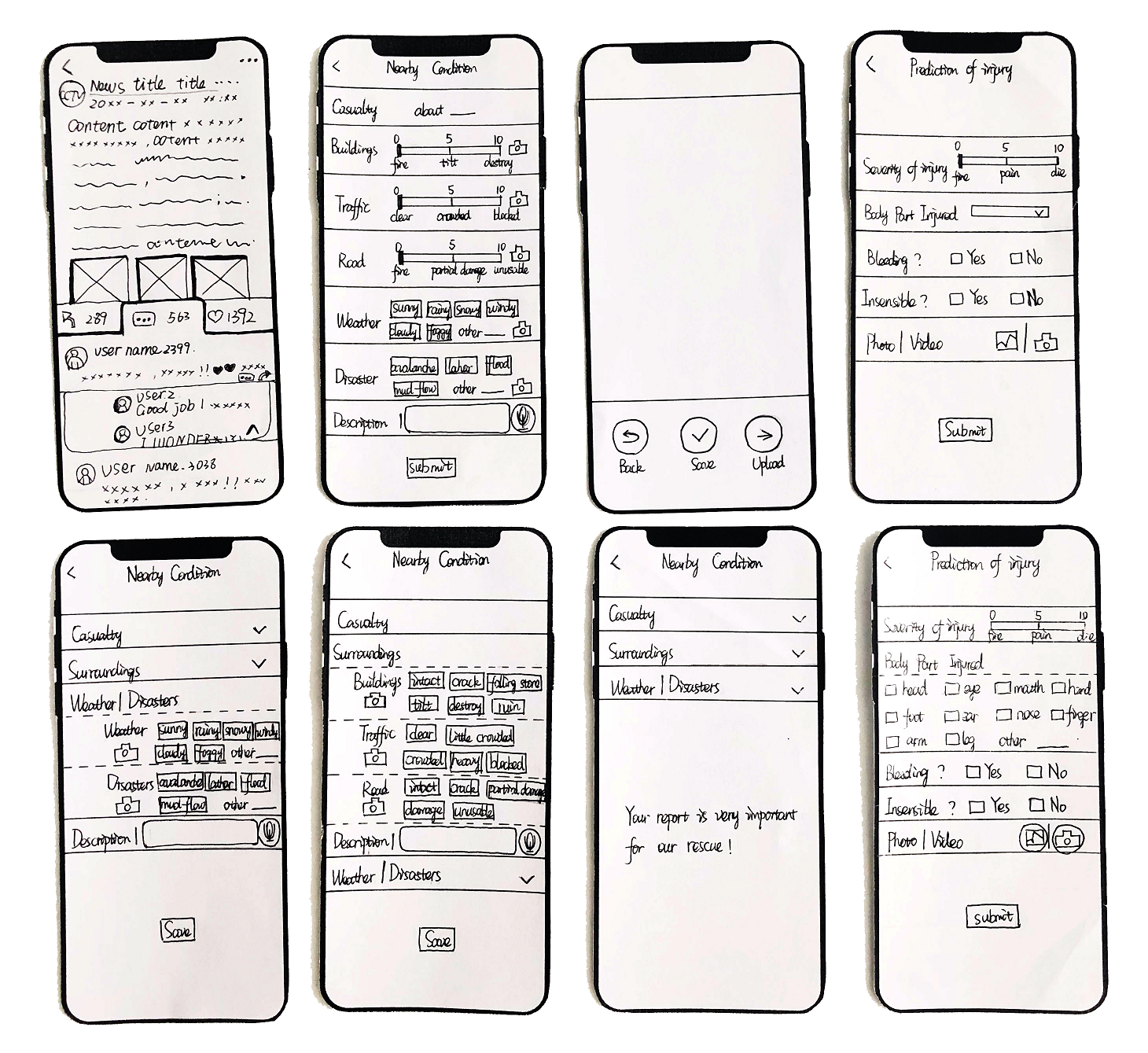
Report functions are complex and confusing. In the next phase, report information would be divided into 4 methods, including description (text and voice), image (photos and videos), score (drag slider), and positioning.
Public User Task Flow
The wounded use it to:
Find a safe place
Check the news
Help others
Connect with rescuers
Report injury situation
Report nearby condition
The government use it to:
View nearby condition
Release news
View the resources and release tasks
Looking for the wounded
View injury situation